Along the widespread of photovoltaic systems for producing electrical power, one of the most important alternative energy markets of last ten years, awareness has grown that the yield of a plant depends not only on the quantity of cell installed, on their placement and on the characteristics of the plant, but it depends also on environmental factors among which, the most important, the real solar radiation.
Producers of photovoltaic energy are well aware that a warm sunny day is not enough for a high yield of a plant, but the highest yields are obtained during the Spring season, when the sky is free of smog, water particles and anything else might hinder the solar radiation.
This awareness leads to the need to continuously monitor the real radiation by using monitoring systems equipped whit high sensitive pyranometers that, together with other environmental data such as air temperature, temperature of photovoltaic cell, humidity and eventual rain fall, wind and pressure, provide a data collection that, once processed, allow you to obtain the real yield of the plant and/or the single cell.
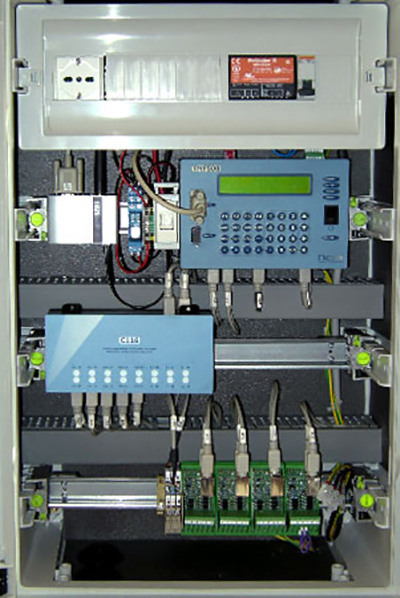
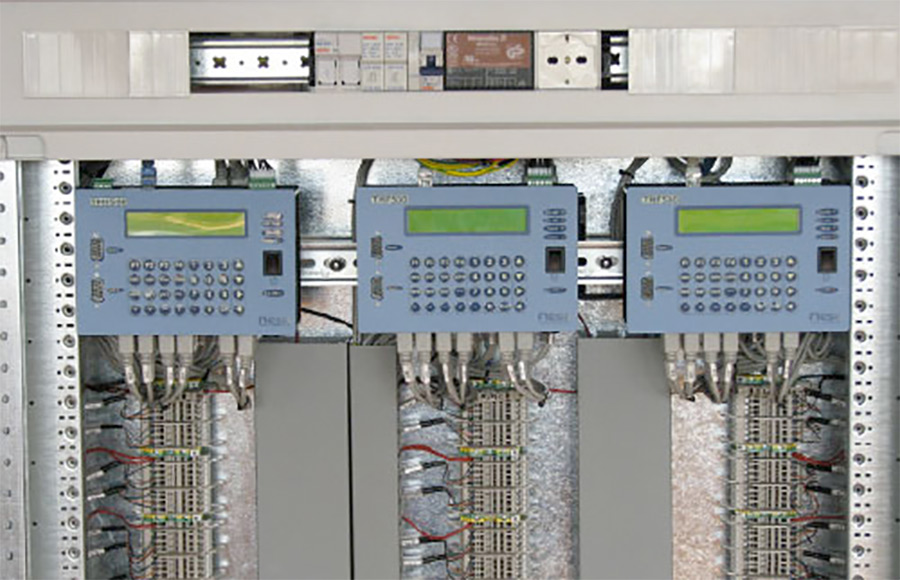
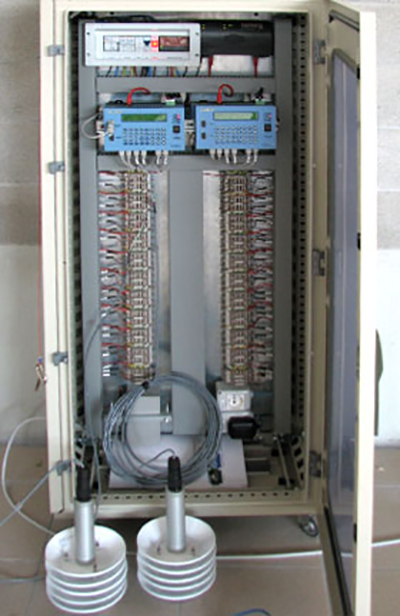
Nesa is able to provide all the expertise needed for this type of monitoring, thanks to the collaboration with one of the leading European research institute on radiometry, ISAC in Bologna. We developed the ST9060, a radiometric monitoring system which is specific for this type of plants. It is composed of radiometers with different accuracy classes (1st class, 2nd class, secondary standard), datalogger for detecting and processing data and all the equipment for environmental monitoring.
All the instruments are certified. The whole system is in according with both WMO norms and IEC 60904. In addition to the data acquisition, Nesa in one of the few companies who uses in its systems the astronomical calculation for the sun position (azimuth and zenith), in function of the geographic location of the plant and the inclination of panels.
This calculation is necessary because the pyranometer is a sensor that detects radiation from the whole sky, while photovoltaic panels only the orthogonal radiation to the panel’s surface. Furthermore, since the sun does not maintain a fixed position during the day, the radiation changes and so it should be measured.
The system as composed, provides maximum guarantees in terms of security and reliability of the information, a sort of black box.
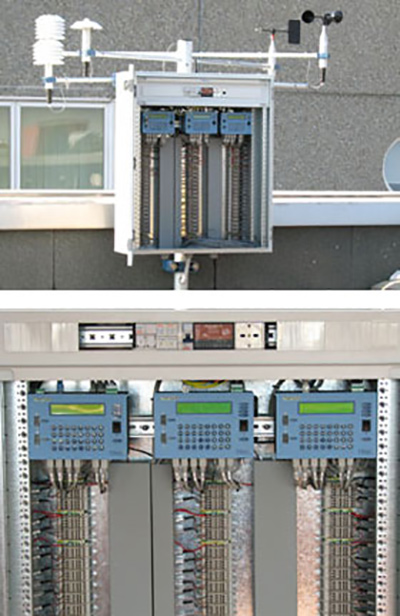
Our experience is confirmed by the major laboratories for the certification of plants and photovoltaic cells in Italy, who uses our solutions, for example IrcCOS in Milano, Associazione Industriali di Brescia, University of Sannio, Sardegna Ricerche and many others.
Our equipment, professional and high performance, is used to test and verify both single cells (IrcCOS) and environmental conditions of photovoltaic plants.
Nesa as manufacturer of its instrumentation, is able to provide customized solutions and to assist customers at every step.
Our systems are able to acquire a practically unlimited number of sensors, allowing a large amount of data with small dimensions. Our datalogger, that you can interface and configure via web, guarantees the highest performance.
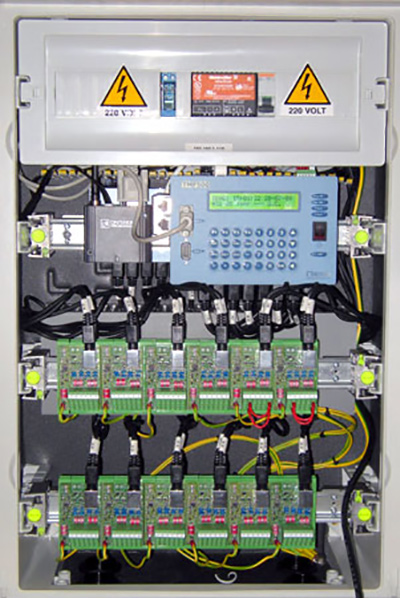
Since 2010 we introduced a new series of wireless instruments with the same performance of those wired, but with the advantage of not having to lay any cable that, given the high number of sensors to monitor for this kind of plant, some time could become a problem.
With one wireless system you can acquire up to about 100 sensors without laying any cable. The new datalogger WLP50 made for these applications, provide the same performances of TMF series but with smaller dimensions and greater potential for calculation.
Our processing software can display data in numerical and graphical format, allowing you to control data in real-time by using simple web pages, available from any internet browser.